Finanarepublic: A Subscription-based Financial Content Platform
Project Summary
Finanarepublic is a full-stack web application built with Next.js, Supabase, and Stripe.
It serves as a content platform for financial news and articles, offering both free and premium content to users. The project features a robust user authentication system, a seamless subscription model for premium access, and a focus on user experience and retention through features like personalized content and saved articles.
Key Features
- User Authentication: Secure sign-up, sign-in, and session management using Supabase Auth.
- Premium Subscriptions: Integration with Stripe to handle monthly and yearly subscriptions, unlocking access to premium articles.
- Content Delivery: A dynamic article system that serves content from a Supabase database.
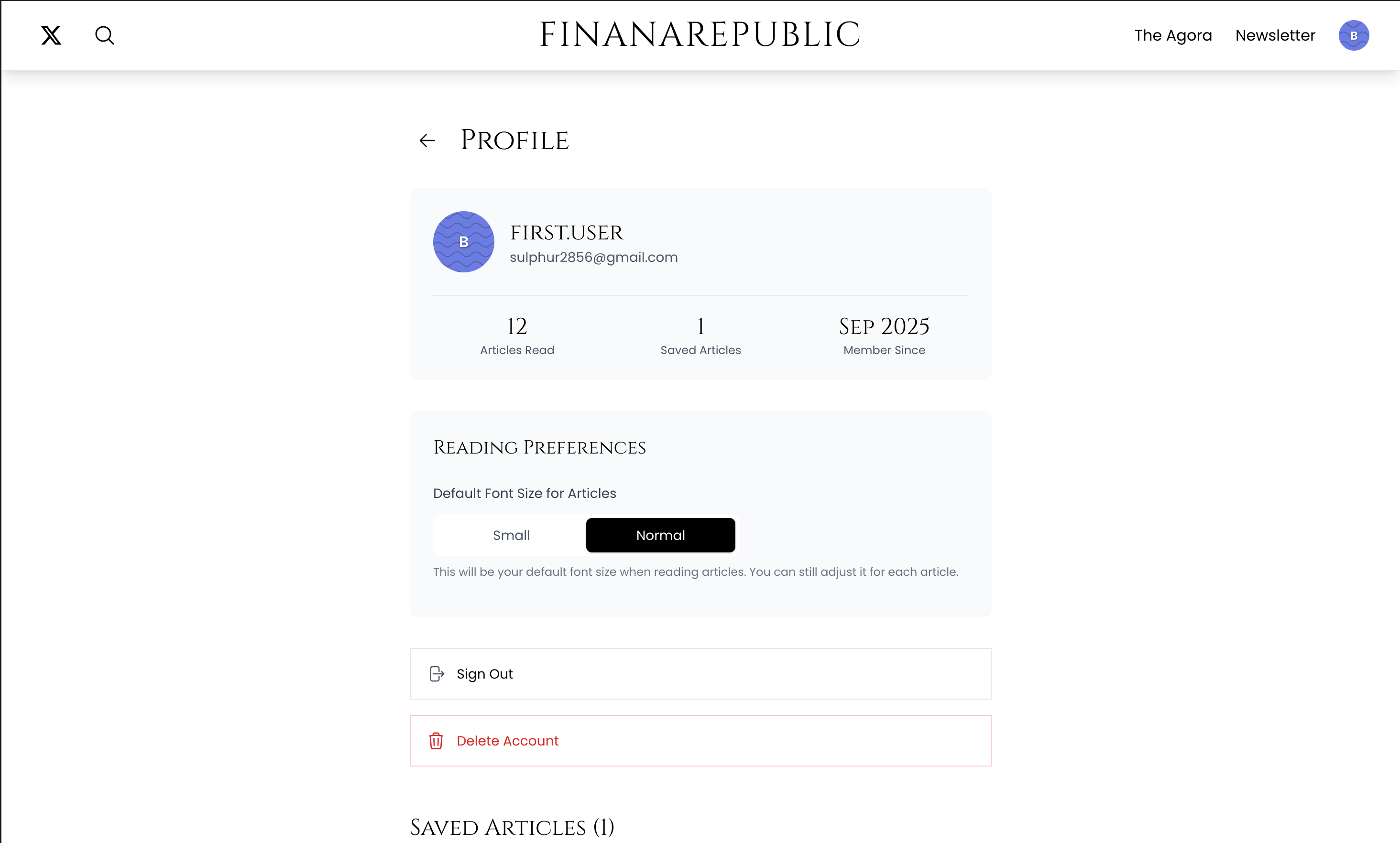
- User Profiles: A dedicated profile section for users to manage their information.
- Saved Articles & Comments: Users can save articles for later reading and engage in discussions through a comments section.
- Responsive Design: A clean, minimalistic, and responsive UI built with Tailwind CSS.
Screenshots
 |
 |
|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Code Implementation Examples
Frontend: Content Viewer Component
The frontend uses client components to handle user-specific logic, such as checking subscription status before rendering an article. This ensures a reactive and secure user experience.
// src/components/ContentViewer.tsx
"use client";
import { useEffect } from "react";
import { useNavigation } from "next/navigation";
import { useUserSession } from "@/hooks/useUserSession";
import { useSubscriptionState } from "@/hooks/useSubscriptionState";
import BodyRenderer from "@/components/BodyRenderer";
import DiscussionForum from "@/components/DiscussionForum";
const ContentViewer: React.FC<{ contentItem: Content }> = ({ contentItem }) => {
const { currentUser } = useUserSession();
const hasActiveSubscription = useSubscriptionState();
const navigation = useNavigation();
// Redirect non-subscribed users from premium content
useEffect(() => {
if (contentItem.requiresSubscription && !hasActiveSubscription) {
navigation.redirectTo("/subscribe");
}
}, [contentItem.requiresSubscription, hasActiveSubscription, navigation]);
if (contentItem.requiresSubscription && !hasActiveSubscription) {
return <p>Redirecting to our subscription page...</p>;
}
return (
<main>
<h1>{contentItem.title}</h1>
<BodyRenderer content={contentItem.body} />
{currentUser && <DiscussionForum contentId={contentItem.id} />}
</main>
);
};
export default ContentViewer;
Backend: Initiating a Payment Session
The backend is built with API Routes (serverless functions). This example shows how an authenticated user can initiate a subscription checkout.
// src/app/api/initiate-payment/route.ts
import { NextApiRequest, NextApiResponse } from "next";
import { initializePaymentProvider } from "@/lib/payment-provider";
import { initializeUserDatabase } from "@/lib/user-database";
export async function handler(
request: NextApiRequest,
response: NextApiResponse
) {
const paymentProvider = initializePaymentProvider();
const userDatabase = initializeUserDatabase();
// 1. Authenticate the user
const authToken = request.headers.authorization?.split(" ")[1];
const { user: currentUser } = await userDatabase.users.get(authToken);
if (!currentUser) {
return response.status(401).json({ message: "User not authenticated" });
}
// 2. Create a payment session
const { planIdentifier } = request.body;
const checkoutLink = await paymentProvider.checkout.createSession({
paymentType: "subscription",
lineItems: [{ plan: planIdentifier, quantity: 1 }],
successUrl: `${process.env.APP_URL}/subscription/success`,
cancelUrl: `${process.env.APP_URL}/subscription`,
metadata: {
userId: currentUser.id, // Securely pass the user ID
},
});
return response.status(200).json({ checkoutUrl: checkoutLink.url });
}
Website Architecture: User Retention & UX
The architecture is designed around the Jamstack principles, using Next.js for static site generation (SSG) and server-side rendering (SSR) to ensure fast page loads. The core strategy for user retention and UX includes:
- Fast, Performant Experience: Next.js provides an optimized user experience out-of-the-box, which reduces bounce rates.
- Personalization: Features like
useFontSizePreferenceallow users to customize their reading experience. TheuseArticleReadshook tracks reading progress, opening possibilities for personalized recommendations. - Engagement Hooks: The ability to save articles (
useSavedArticlesOptimized) and comment (CommentSection.tsx) encourages users to create an account and return to the platform. - Premium Content Model: A portion of the content is marked as
is_premium. This creates a value proposition for users to subscribe, converting casual readers into paying customers. TheusePremiumStatushook seamlessly manages the UI for premium and non-premium users.
Security Architecture
Security is managed at multiple layers: the edge, the application, and the database.
-
Edge & Application Security (Middleware): Next.js Middleware is used to implement crucial security headers on all incoming requests. This provides a first line of defense against common web vulnerabilities.
// src/middleware.ts import { NextResponse, NextRequest } from "next/server"; export function securityMiddleware(request: NextRequest) { const response = NextResponse.next(); // Define a strict Content Security Policy const cspDirectives = [ "default-src 'self'", "script-src 'self' https://trusted-scripts.com", "style-src 'self' https://trusted-styles.com", "img-src 'self' data:", "font-src 'self'", "frame-ancestors 'none'", // Disallow embedding in iframes ].join("; "); response.headers.set("Content-Security-Policy", cspDirectives); // Add other security headers response.headers.set("X-Frame-Options", "DENY"); response.headers.set("X-Content-Type-Options", "nosniff"); response.headers.set( "Referrer-Policy", "strict-origin-when-cross-origin" ); return response; } -
Authentication & Authorization: Handled by Supabase Auth, which uses JWTs (JSON Web Tokens) stored securely in cookies. All API requests that require authentication are validated against the Supabase backend.
-
Database Security: Supabase provides Row Level Security (RLS) on its Postgres database. This ensures that even if an API request is compromised, users can only access or modify data they are permitted to. For example, a user can only update their own profile.
Tools & Technologies
- Framework: Next.js 15
- Programming Language: TypeScript
- Frontend: React 19
- Styling: Tailwind CSS
- Backend-as-a-Service: Supabase (Postgres Database, Auth, Storage)
- Payments: Stripe
APIs and Webhooks
Premium Subscription APIs
The application communicates with the Stripe API through dedicated Next.js API routes:
/api/create-checkout-session: Authenticates a user and creates a Stripe session to redirect them to a secure payment page./api/cancel-subscription: Allows a user to cancel their active subscription.
Stripe Webhooks
The /api/stripe-webhook endpoint is a critical component that listens for events from Stripe. This allows the application to react to real-world payment events asynchronously.
checkout.session.completed: When a user successfully subscribes, this event is triggered. The webhook verifies the event, extracts theuser.idfrom the session metadata, and updates the corresponding user record in the Supabase database to grant premium access (is_premium = true).customer.subscription.deleted: When a subscription is canceled or expires, this event is used to revoke premium access for the user.
This webhook is secured by verifying the Stripe signature and uses the Supabase Service Role Key for admin-level database operations.
// src/app/api/payment-webhook/route.ts
import { initializePaymentProvider } from "@/lib/payment-provider";
import { initializeAdminDatabase } from "@/lib/user-database";
const paymentProvider = initializePaymentProvider();
const appDatabase = initializeAdminDatabase(); // Use admin rights
export async function handleWebhookEvent(request: Request) {
const webhookSignature = request.headers.get("Payment-Provider-Signature");
const rawBody = await request.text();
// 1. Verify the event originated from the payment provider
const webhookPayload = paymentProvider.webhooks.verifySignature(
rawBody,
webhookSignature,
process.env.WEBHOOK_SIGNING_SECRET
);
// 2. Handle the specific event
switch (webhookPayload.type) {
case "payment.successful":
const paymentDetails = webhookPayload.data;
const customerId = paymentDetails.metadata.userId;
// 3. Update user's subscription status in the database
if (customerId) {
await appDatabase.users.updateSubscription({
userId: customerId,
isSubscribed: true,
subscriptionId: paymentDetails.subscriptionId,
});
}
break;
case "subscription.cancelled":
// Handle cancellation logic...
break;
}
return new Response("Webhook processed", { status: 200 });
}
Database, Authentication, and User Management
Database
The backend uses a Supabase Postgres database. The schema is designed to support the application's features, with tables for users, articles, comments, saved_articles, etc.
Authentication and Session Management
Authentication is handled entirely by Supabase Auth.
- A user signs up or logs in via the Supabase client.
- Supabase returns a JWT (access token) and a refresh token.
- These tokens are automatically stored in secure,
HttpOnlycookies by the Supabase SSR library, ensuring they cannot be accessed by client-side JavaScript. - The access token is sent in the
Authorizationheader for API calls, and the middleware/API routes validate it. - The session is automatically refreshed using the refresh token.
User Management
- Creating Users: Users are created via the standard Supabase sign-up flow. A new entry is added to the
auth.userstable, and a trigger typically copies public-safe information to apublic.userstable. - Modifying Users: Users can modify their own data through protected API endpoints that enforce permissions using RLS policies (e.g.,
...where auth.uid() = user_id). - Deleting Users: The project includes a SQL function (
delete_user_account_function.sql) that can be called from a protected endpoint. This function securely deletes a user's data from all relevant tables, including their auth entry. - Creating Content: Authors use a separate, restricted interface (not detailed in the provided files, but implied by the architecture) to create and manage articles in the
articlestable. Users can createcommentswhich are linked to theiruser_idand anarticle_id.
Cookie Management
Cookie management is abstracted away by the supabase-js SSR library.
- Session Cookies: The primary cookies are
sb-access-tokenandsb-refresh-token. They are configured asHttpOnlyandSecurein production, making them inaccessible to XSS attacks. - CSRF Protection: The application includes a
/api/csrfroute, suggesting a Double Submit Cookie pattern or similar mechanism is used to prevent Cross-Site Request Forgery attacks on form submissions.
Design Philosophy
The project follows a minimalistic and content-first design philosophy.
- Clean UI: The interface is kept simple and uncluttered to focus the user's attention on the content.
- Typography: Emphasis is placed on readability, with clear fonts and customizable font sizes.
- Utility-First CSS: Tailwind CSS is used to rapidly build a consistent and responsive design system without writing custom CSS.